Class 12 Physics Chapter 2: In Class 12 Physics Chapter 2, students learn about electrostatic potential, how charges create potential, and how capacitors store energy. We learn with “class 12 physics chapter 2 notes,” “ncert solutions for class 12 physics chapter 2,” and step-by-step answers that help in exams. Chapter 2 physics class 12 NCERT solutions make every topic easy. All the important ideas are explained, so you can understand and score better.
Class 12 Physics Chapter 2 Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance Sub Topics
This table shows all sub-topics, a story/concept name to remember, and the main thing you learn.
| Sub-topic | Story/Concept Name | Main Learning/Moral |
|---|---|---|
| Electrostatic Potential | Hill Climb | Work is needed to bring charge close to other charges |
| Potential due to a Point Charge | Light Bulb | One charge makes potential at a distance |
| Potential due to an Electric Dipole | The Double Star | Two close charges make special potential |
| Potential due to System of Charges | The Family | Many charges create combined potentials |
| Equipotential Surfaces | Flat Playground | Spots with same potential are flat |
| Potential Energy of System | Filling a Tank | Energy stored depends on charge positions |
| Potential Energy in External Field | Pushing a Swing | Field helps store extra energy |
| Electrostatics of Conductors | Safe Tunnel | Charges stay on surface, inside is calm |
| Dielectrics and Polarisation | Sponge Ball | Sponge material gets soft charge inside |
| Capacitors and Capacitance | Water Bottle | Stores charge, has capacity |
| Parallel Plate Capacitor | Sandwich Plate | Two plates store charge between them |
| Effect of Dielectric on Capacitance | Magic Cloth | Special materials help store more charge |
| Combination of Capacitors | Teamwork | Many bottles together hold more or less charge |
| Energy Stored in Capacitor | Fuel Tank | Capacitor stores energy like a tank |
NCERT Solution for Class 12 Physics Chapter 2
Here are detailed answers to all exercise questions. All steps are easy and equations are given so you can copy and use.
Q1. Two charges 5×10−8 C and −3×10−8 C are located 16 cm apart. At what point(s) on the line joining the two charges is the electric potential zero? Take the potential at infinity to be zero.
Let charge 1 (q₁) = 5 × 10⁻⁸ C at x = 0
Let charge 2 (q₂) = −3 × 10⁻⁸ C at x = 0.16 m
Potential at a point P, distance r from q₁ and (0.16 − r) from q₂:
V = k q₁ / r + k q₂ / (0.16 − r)
Set V=0:
r / q₁ = −(0.16 − r) / q₂
5 × 10⁻⁸ / r = 3 × 10⁻⁸ / (0.16 − r)
(5 × 10⁻⁸) / r = (0.16 − r) / (3 × 10⁻⁸)
5(0.16 − r) = 3r
0.8 − 5r = 3r
8r = 0.8
r = 0.1
So, the potential is zero at r = 0.1 m (10 cm) from q₁.
Q2. A regular hexagon of side 10 cm has a charge 5 mC at each vertex. Calculate the potential at the centre.
Potential at centre due to one charge:
V = kq / r
Distance from centre to each vertex:
r = 10 cm = 0.1 m
Total potential due to 6 equal charges:
Vₜₒₜₐₗ = 6 × (9 × 10⁹ × 5 × 10⁻³) / 0.1
= 6 × (45 × 10⁶) / 0.1
= 6 × (4.5 × 10⁸)
= 2.7 × 10⁹ V
Q3. Two charges 2 mC and –2 mC are placed at points A and B 6 cm apart.
(a) An equipotential surface is a surface where the potential is same everywhere. Between these charges, the surface perpendicular to the line AB and passing through the midpoint is an equipotential surface.
(b) The electric field at every point on this surface points from positive charge to negative charge (from A to B).
Q4. A spherical conductor of radius 12 cm has a charge of 1.6×10−7 C distributed uniformly. What is the electric field
(a) Inside the sphere:
Electric field inside = 0
(b) Just outside the sphere:
E = (1 / 4πϵ₀) × (Q / r²)
= 9 × 10⁹ × 1.6 × 10⁻⁷ / (0.12)²
= 1.44 × 10³ / 0.0144
= 1 × 10⁵ N/C
(c) At a point 18 cm from the centre:
E = 9 × 10⁹ × 1.6 × 10⁻⁷ / (0.18)²
= 1.44 × 10³ / 0.0324
= 4.44 × 10⁴ N/C
Q5. A parallel plate capacitor with air between the plates has capacitance 8 pF. What is the capacitance if the distance is halved and space filled with dielectric of constant 6?
Original:
C = ε₀ A / d
New conditions:
-
Distance halved → d_new = d / 2
-
Dielectric constant → K = 6
Therefore:
C_new = K × ε₀ × A / d_new
Q6. Three capacitors each 9 pF in series.
(a) Total capacitance:
C total = 3C = 3 pF
(b) Voltage across each capacitor:
Each capacitor gets voltage = total voltage / 3
If connected to 120 V:
V each = 120 / 3 = 40 V
Q7. Three capacitors 2 pF, 3 pF, 4 pF in parallel.
(a) Total capacitance:
C total = 2 + 3 + 4 = 9 pF
(b) Charge on each capacitor:
Using Q = C V
For V = 100 V:
-
2 pF:
Q₁ = 2 × 100 = 200 pC -
3 pF:
Q₂ = 3 × 100 = 300 pC -
4 pF:
Q₃ = 4 × 100 = 400 pC
Q8. Parallel plate capacitor with air, each plate area 6×10−3 m², distance 3 mm. Calculate capacitance and charge for 100 V.
C = ε₀ A / d
= 8.85 × 10⁻¹² × 6 × 10⁻³ / 3 × 10⁻³
= 8.85 × 10⁻¹² × (6 × 10⁻³ / 3 × 10⁻³)
= 8.85 × 10⁻¹² × 2
= 17.7 × 10⁻¹² F
= 17.7 pF
Charge:
Q = C V
= 17.7 × 10⁻¹² × 100
= 1.77 × 10⁻⁹ C
Q9. What happens if in Q8, a 3 mm mica sheet (K=6) is inserted
(a) When supply connected:
Capacitance rises to K. Charge increases because V is fixed.
(b) After supply disconnected:
Charge stays same, voltage drops to maintain Q = C₍new₎ × V₍new₎
Q10. A 12 pF capacitor is connected to a 50 V battery. How much energy stored?
E = ½ C V²
= 0.5 × 12 × 10⁻¹² × (50)²
= 0.5 × 12 × 10⁻¹² × 2500 = 0.5 × 30 × 10⁻⁹ = 15 × 10⁻⁹ = 1.5 × 10⁻⁸ J
Q11. 600 pF capacitor charged by 200V, disconnected, connected to an uncharged 600 pF capacitor. How much energy lost?
Initial energy:
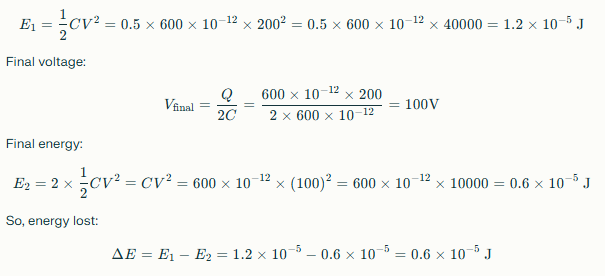
Class 12 physics chapter 2 Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance PDF
This PDF helps you study all “physics class 12 chapter 2” topics in one file. You get clear answers, formulas, and all “class 12 physics chapter 2 exercise solutions” for exams. Save and use the PDF to revise anytime; our blog is also shared in PDF format for simple revision.
Physics Class 12 Chapter 2 Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance Summary
Get the topic wise summary of Class 12 Physics Chapter 2 Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance Summary:
- Electrostatic Potential: Electrostatic potential shows how much work is done to bring a charge from far away to a point.
- Potential due to a Point Charge: One charge gives potential everywhere around it. The closer you go, the bigger the potential.
- Potential due to an Electric Dipole: Two opposite charges close together make special patterns of potential.
- Potential due to a System of Charges: Many charges create complex potentials. You add up each charge’s effect at a point.
- Equipotential Surfaces: These are imaginary flat spots where potential is always same. No work is done moving along them.
- Potential Energy of a System: More charges need more energy. Energy is stored when you move charges near each other.
- Potential Energy in External Field: When an outside field is present, the system stores extra energy.
- Electrostatics of Conductors: Charges settle only on the surface. Inside a closed conductor, everything stays calm.
- Dielectrics and Polarisation: Dielectrics are materials that change how charges behave. They get tiny charges inside and help store more charge.
- Capacitors and Capacitance: A capacitor stores charge, and capacitance measures how much it can hold.
- Parallel Plate Capacitor: Two plates make a capacitor. The smaller the gap, the bigger the capacitance.
- Effect of Dielectric on Capacitance: Using special materials in between plates makes the capacitor store even more charge.
- Combination of Capacitors: Capacitors can be joined together. Teamwork makes total capacity go up or down.
- Energy Stored in Capacitor: Capacitor stores energy so it can be used later, just like a fuel tank.
How to Learn class 12 Physics Chapter 2 Easily
Follow these easy tips to learn the chapter quickly and remember it for exams.
- Divide Into Parts: Focus on each sub-topic one by one to make learning easy.
- Note Important Points: Write out formulas and key ideas for quick revision.
- Practice All Questions: Solve exercise solutions and examples to build confidence and speed.
- Share Concepts as Stories: Tell your friend what you learned using your own words.
- Connect with Daily Life: Find capacitors and charges in gadgets around you (TV, phone, computer).
Physics Class 12 Chapter 2 FAQs
Q1: How many sub-topics are in this chapter?
Ans. 14 sub-topics are included, each teaching a special idea about potential and capacitance.
Q2: What is the main lesson of this chapter?
Ans. The chapter teaches how charges create energy and how we can store and use this energy safely.
Q3: Which part is most important?
Ans. Parallel plate capacitor and energy stored in capacitors are important for many exams.
Q4: How will the chapter help in future study?
Ans. This chapter gives the base to study electric circuits and electronics.
Q5: How do I use class 12 physics chapter 2 exercise solutions?
Ans. Use the step-by-step answers and copy the equations as shown above to get good marks.
